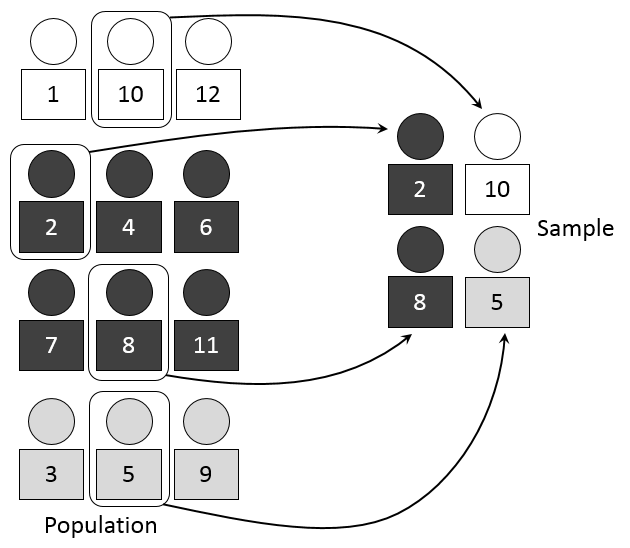
Simple Random Sampling In the Simple random sampling method each unit included in the sample has equal chance of inclusion in the sample. It is also called probability sampling.
Here P is a probability n is the sample size and N represents the population.
Random sampling formula statistics. Random sampling is a method of choosing a sample of observations from a population to make assumptions about the population. It is also called probability sampling. The counterpart of this sampling is Non-probability sampling or Non-random sampling.
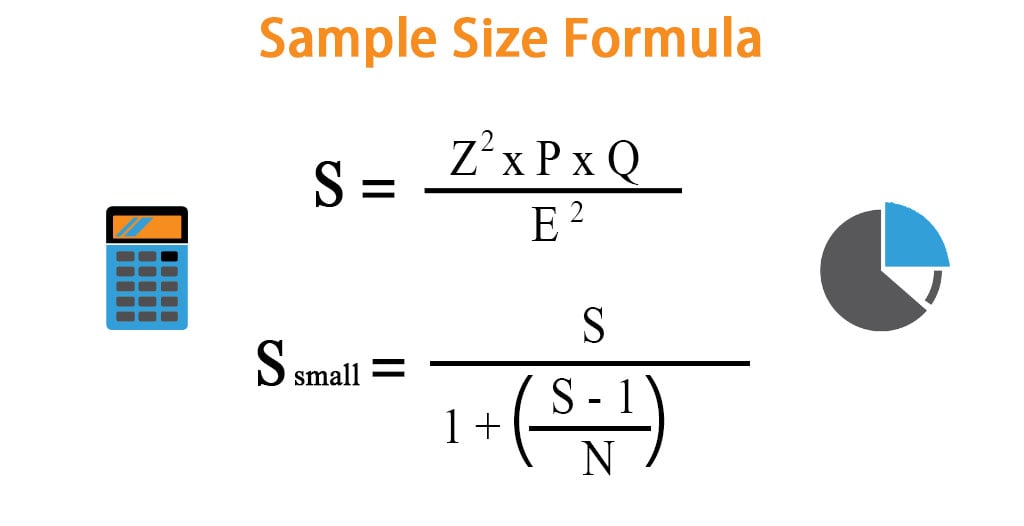
Required sample size need to achieve an allowable error E expressed as a desired half-width of a confidence interval eg. 500 or allowable error percent A expressed as a percent of the mean eg 10. Sampling with Replacement or from infinite population Sampling.
The Formula of Random Sampling The formula of random sampling is if that sample gets selected only once P 1 N-1NN-2N-1N-nN-n-1. Here P is a probability n is the sample size and N represents the population. The three will be selected by simple random sampling.
The mean for a sample is derived using Formula 34. 34 where xi is the number of intravenous injections in each sampled person and n is the number of sampled persons. For example assume that Roy-Jon-Ben is the sample.
Roy had 12 intr avenous drug injections during the past two weeks. A simple random sample is defined as one in which each element of the population has an equal and independent chance of being selected. In case of a population with N units the probability of choosing n sample units with all possible combinations of N Cn samples is given by 1N Cn eg.
What Is Systematic Random Sampling. Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population. Simple random sampling is a type of probability sampling in which the researcher randomly selects a subset of participants from a population.
Each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. Data is then collected from. The fourth formula Neyman allocation uses stratified sampling to minimize variance given a fixed sample size.
And the last formula optimum allocation uses stratified sampling to minimize variance given a fixed budget. Mean simple random sampling. N z 2 σ 2 N N -.
As the division of sub-groups or strata and a total sample is taken to represent the entire population depends upon the researcher there is no specific formula for Stratified Random Sampling. But the formula mentioned below is used widely. Stratified Random Sampling Formula Total Sample Size Entire Population Population of Subgroups.
What is Random Variable in Statistics. In probability a real-valued function defined over the sample space of a random experiment is called a random variableThat is the values of the random variable correspond to the outcomes of the random experiment. Simple Random Sampling In the Simple random sampling method each unit included in the sample has equal chance of inclusion in the sample.
This technique provides the unbiased and better estimate of the parameters if the population is homogeneous. Calculate the sample of each grade using the stratified random sampling formula. Stratified Sample n5 100 1000 150 15 Stratified Sample n6 100 1000.
Slovins formula calculates the number of samples required when the population is too large to directly sample every member. Slovins formula works for simple random sampling. If the population to be sampled has obvious subgroups Slovins formula could be applied to each individual group instead of the whole group.
Consider the example problem. Calculate sampling interval k Nn. Select a random number between 1 to k including k Add the sampling interval k to the chosen random number to add the next member to a sample and repeat this procedure to add remaining members of the sample.
In case k isnt an integer you can select the closest integer to Nn.