It allows us to compare data make hypothesis and predictions. On the contrary in Inferential statistics researchers test the hypothesis.
Youll need to account for the deadlines you have for research and development to choose which statistic is more viable for you.
Definition of descriptive and inferential statistics. In summary statistics is categorized into two branches - descriptive and inferential. Descriptive statistics uses the data to provide descriptions of the population either through numerical. Descriptive statistics use summary statistics graphs and tables to describe a data set.
This is useful for helping us gain a quick and easy understanding of a data set without pouring over all of the individual data values. Inferential statistics use samples to draw inferences about larger populations. Descriptive statistics describe what is going on in a population or data set.
Inferential statistics by contrast allow scientists to take findings from a sample group and generalize them to a larger population. The two types of statistics have some important differences. In brief Descriptive statistics analyze the big data with the help of charts and tables.
It never attempts to use a sample to reach a conclusion. On the contrary in Inferential statistics researchers test the hypothesis. Heshe studies the sample and reaches the conclusions of the population.
This blog is based on Descriptive and Inferential statistics. So what are descriptive and inferential statistics. And what are their differences.
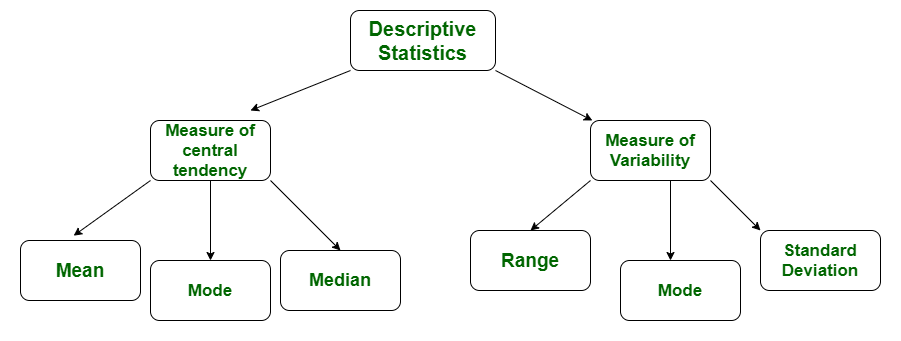
Descriptive statistics is the term given to the analysis of data that helps describe show or summarize data in a meaningful way such that for example patterns might emerge from the data. In this type of statistics the data is summarised through the given observations. The summarisation is one from a sample of population using parameters such as the mean or standard deviation.
Descriptive statistics is a way to organise represent and describe a collection of data using tables graphs and summary measures. When analysing data such as the grades earned by 100 studentsit is possible to use both descriptive and inferential statisticsin your analysis. Typically in most research conducted ongroups of people you will use both descriptive and inferential statistics toanalyse your results and draw conclusions.
So what are descriptive andinferential statistics. And what are their differences. Descriptive and inferential statistics are both statistical procedures that help describe a data sample set and draw inferences from the same respectively.
The ScienceStruck article below enlists the difference between descriptive and inferential. We first describe methods of descriptive statistics which enable to capture the important features from sample data using tables charts and graphs. Then the described sampling distributions pave the way to inferential statistics which allows us to draw conclusions about the whole population from which we took the sample.
Descriptive statistics is the term given to the analysis of data that helps describe show or summarize data in a meaningful way such that for example patterns might emerge from the data. They provide simple summaries about the sample and the measures. These very useful statistics bring together large amounts of data.
Descriptive statistics are used to describe the general conditions and characteristics of the data while inferential statistics are used to draw conclusions. The primary difference between descriptive and inferential statistics is that descriptive statistics measure for definitive measurement while inferential statistics note the margin of error of research performed. Youll need to account for the deadlines you have for research and development to choose which statistic is more viable for you.
Descriptive Statistics Inferential Statistics. It gives information about raw data which describes the data in some manner. It makes inference about population using data drawn from the population.
It helps in organizing analyzing and to present data in a meaningful manner. It allows us to compare data make hypothesis and predictions. Descriptive Statistics Both descriptive and inferential statistics help make sense out of row after row of data.
Use descriptive statistics to summarize and graph the data for a group that you choose. This process allows you to understand that specific set of observations. Descriptive Statistics is a discipline which is concerned with describing the population under study.
Inferential Statistics is a type of statistics. That focuses on drawing conclusions about the population on the basis of sample analysis and observation. Descriptive Statistics collects organises analyzes and presents data in a meaningful way.
Definition of Descriptive Statistics. Descriptive statistics is defined as a brief quantifiable summary that explains a given amount of data that represents a complete set of information or a sample of it. It is expressed mostly in numbers which are concluded from a.