
This is because the binomial distribution. The binomial distribution is frequently used to model the number of successes in a sample of size n drawn with replacement from a population of size N.
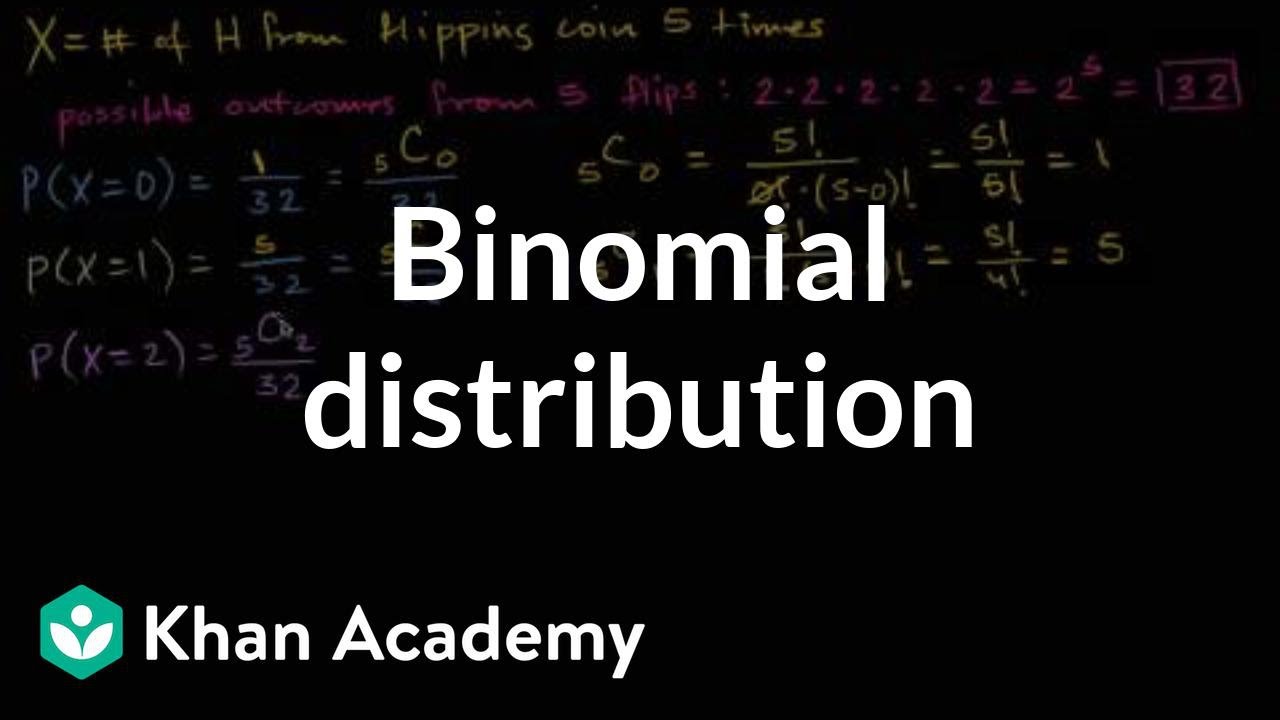
Binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution which expresses the probability of one set of two alternatives-successes p and failure q.
Binomial distribution in statistics. Binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution which expresses the probability of one set of two alternatives-successes p and failure q. Binomial distribution is defined and given by the following probability function. In probability theory and statistics the binomial distribution is the discrete probability distribution that gives only two possible results in an experiment either Success or Failure.
For example if we toss a coin there could be only two possible outcomes. Heads or tails and if any test is taken then there could be only two results. The binomial distribution function also has a nice relationship to the beta distribution function.
A binomial distribution can be thought of as simply the probability of a SUCCESS or FAILURE outcome in an experiment or survey that is repeated multiple times. The binomial is a type of distribution that has two possible outcomes the prefix bi means two or twice. The Binomial probability distribution with parameters n and p sometimes denoted Binomial np or Binom np is a discrete probability distribution.
It describes a type of random number X that can equal anything from 0 up to n. The formula for this probability distribution is. The outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial probability distribution.
The random variable X X the number of successes obtained in the n independent trials. The mean μ μ and variance σ2 σ 2 for the binomial probability distribution are μ np μ n p and σ2 npq σ 2 n p q. In the equation for the binomial X.
Is the factorial function ie multiply all whole numbers from 1 to X and for the normal distribution exp refers to the exponential function which we discussed in the Chapter on Data Handling. Binomial distribution with R Below an intro to the R functions dbinom pbinom rbinom and qbinom functions. On the page The binomial distribution in R I do more worked examples with the binomial distribution in R.
For the next examples say that X is binomially distributed with n20 trials and p16 prob of success. The binomial distribution is frequently used to model the number of successes in a sample of size n drawn with replacement from a population of size N. Three characteristics of a binomial experiment.
The binomial distribution is a common discrete distribution used in statistics as opposed to a continuous distribution such as the normal distribution. This is because the binomial distribution.